What are Industrial Design Rights?
Industrial Design Rights are legal protections for the visual aspects of a product, such as its shape, pattern, or color combination, which add aesthetic value and distinguish the product from others. In the business world, registered product designs provide competitive advantages and protect against imitation by third parties.
This article will discuss 12 examples of products that implement Industrial Design Rights across various sectors, including technology, automotive, fashion, as well as healthcare and the chemical industry, which are often overlooked.
Examples of Industrial Design Rights: Implementation in 12 Products
1. Red Bull
This is an example of industrial design rights for energy drink bottles.
Patented Design: A sleek, iconic can shape with a dominant blue and silver color scheme and the signature logo featuring two bulls facing off.
How It’s Protected: Through Industrial Design Rights, the visual design of the can—including its shape, colors, and logo—is patented, preventing competitors from copying it.
Benefits for the Product:
- Establishes the can design as a recognizable brand identity.
- Protects the product’s authenticity and prevents counterfeiting.
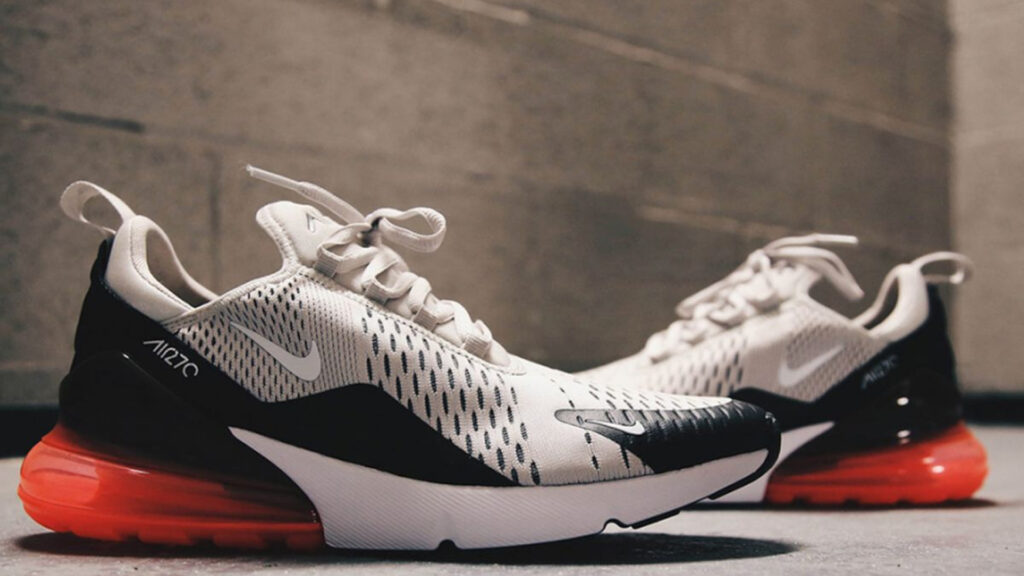
2. Nike Air Max
This is an example of industrial design rights for sport shoes.
Patented Design: Transparent air cushioning unit on the sole and an overall design reflecting advanced technology and high performance.
How It’s Protected: Industrial Design Rights protect the visual elements of the unique sole and the streamlined design of Nike Air Max shoes. The design is also registered widely across major markets for broader protection.
Benefits for the Product:
- Enhances exclusivity and global recognition of Nike products.
- Helps maintain market dominance in the premium sports footwear segment.
3. Apple iPhone
This is an example of industrial design rights for smartphones.
Patented Design: A minimalist appearance with curved edges, thin bezels, and a simple button layout. Distinctive features, like the screen notch, are hallmarks of modern iPhones.
How It’s Protected: Apple applies Industrial Design Rights to safeguard the unique shape, layout, and overall aesthetics of its devices. The protection also includes product packaging.
Benefits for the Product:
- Creates a consistent and globally recognizable brand identity.
- Reduces the risk of competitors mimicking the design.
4. Starbucks
This is an example of industrial design rights for branded coffee cups.
Patented Design: The signature Starbucks disposable cup with its ergonomic shape and recognizable green-and-white logo.
How It’s Protected: Through Industrial Design Rights and Copyrights, the visual design, including its shape, colors, and logo, is registered with an intellectual property organization.
Benefits for the Product:
- Strengthens the global branding of Starbucks with consistent visuals.
- Protects the distinctive cup design from being copied by competitors.
5. Eames Lounge Chair
This is an example of industrial design rights for furniture.
Patented Design: The iconic combination of ergonomic shapes, premium wood finishes, and luxurious leather upholstery.
How It’s Protected: The original design is protected via international Industrial Design registrations, particularly for premium markets.
Benefits for the Product:
- Ensures exclusivity in design, sustaining its premium pricing.
- Establishes the chair as a symbol of style and modern aesthetics.
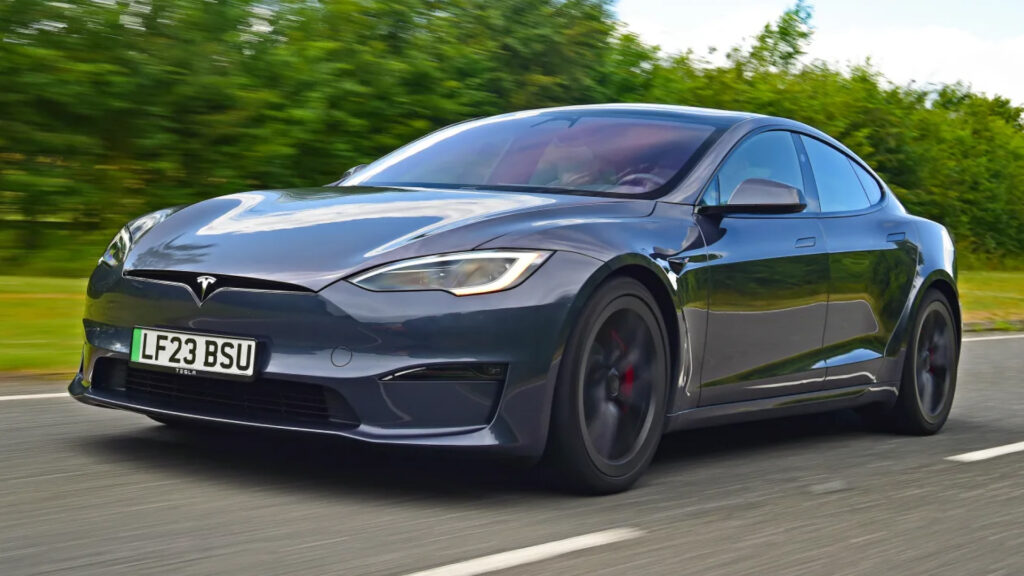
6. Tesla Model S
This is an example of industrial design rights for electric car.
Patented Design: An aerodynamic exterior with smooth lines and a minimalist, futuristic cabin interior.
How It’s Protected: Tesla registers the visual design of its car’s interior and exterior under Industrial Design Rights in multiple major jurisdictions worldwide.
Benefits for the Product:
- Positions the Tesla brand as a leader in premium and innovative electric cars.
- Protects design elements from being replicated by other manufacturers.
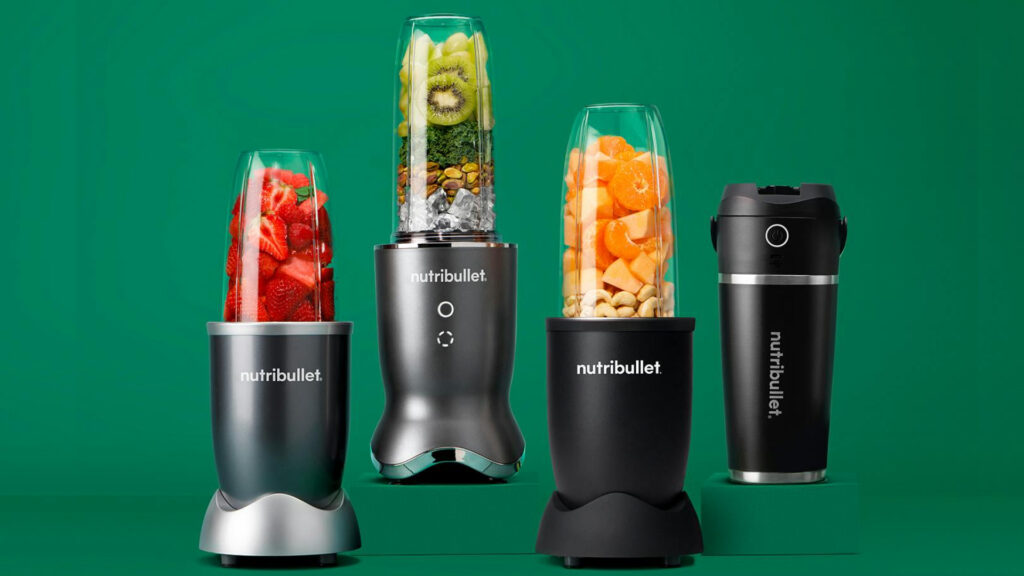
7. NutriBullet Blender
This is an example of industrial design rights for kitchen appliances.
Patented Design: A compact blender design with integrated blades inside the container for ease of use.
How It’s Protected: Industrial Design Rights protect the product’s overall shape, appearance, and visual systems.
Benefits for the Product:
- Builds consumer trust based on exclusive and user-centric design.
- Differentiates NutriBullet from conventional blenders.
8. Lego
This is an example of industrial design rights for children’s toys.
Patented Design: Plastic building blocks with a unique “interlocking” system and visually distinctive color elements.
How It’s Protected: Lego safeguards its visual design elements through Industrial Design Rights, preventing imitation of the blocks’ shapes or overall design.
Benefits for the Product:
- Secures Lego’s status as the leader in the toy market.
- Increases appeal and exclusivity among children and collectors.
9. GoPro Hero
This is an example of industrial design rights for digital cameras.
Patented Design: A compact, waterproof casing with modular design features and impact-resistant materials.
How It’s Protected: GoPro protects its casing design via Industrial Design Rights and registers its visual elements globally.
Benefits for the Product:
- Establishes GoPro as an iconic brand in the action camera market.
- Builds consumer trust in product authenticity and quality.
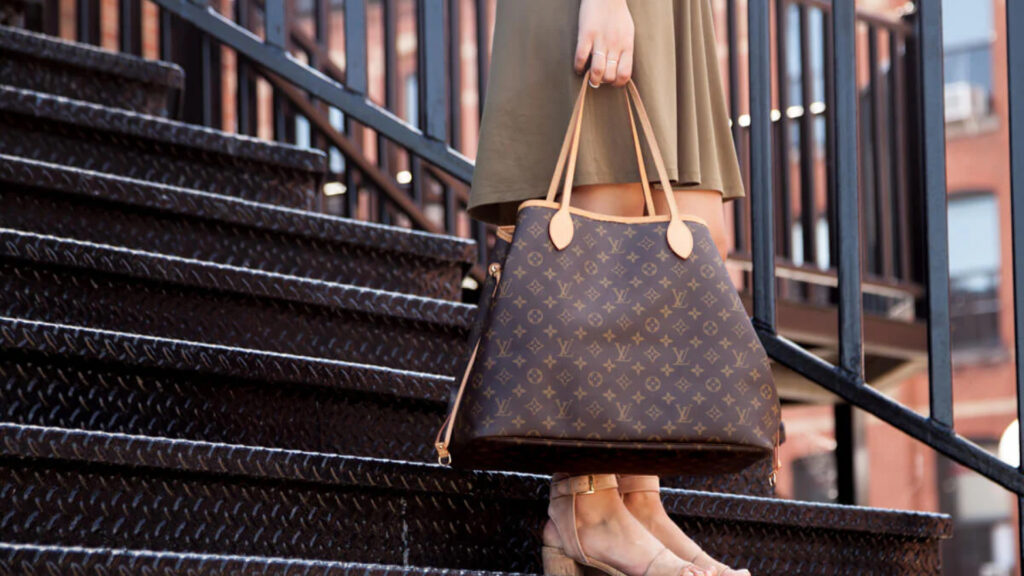
10. Louis Vuitton Tote
This is an example of industrial design rights for fashion bags.
Patented Design: The LV monogram pattern paired with classic brown tones and metal ornaments.
How It’s Protected: The pattern, shape, and other visual elements are protected under Industrial Design Rights, ensuring the bag’s exclusivity.
Benefits for the Product:
- Maintains its premium appeal to high-end consumers.
- Prevents counterfeiting, which is common for luxury products.
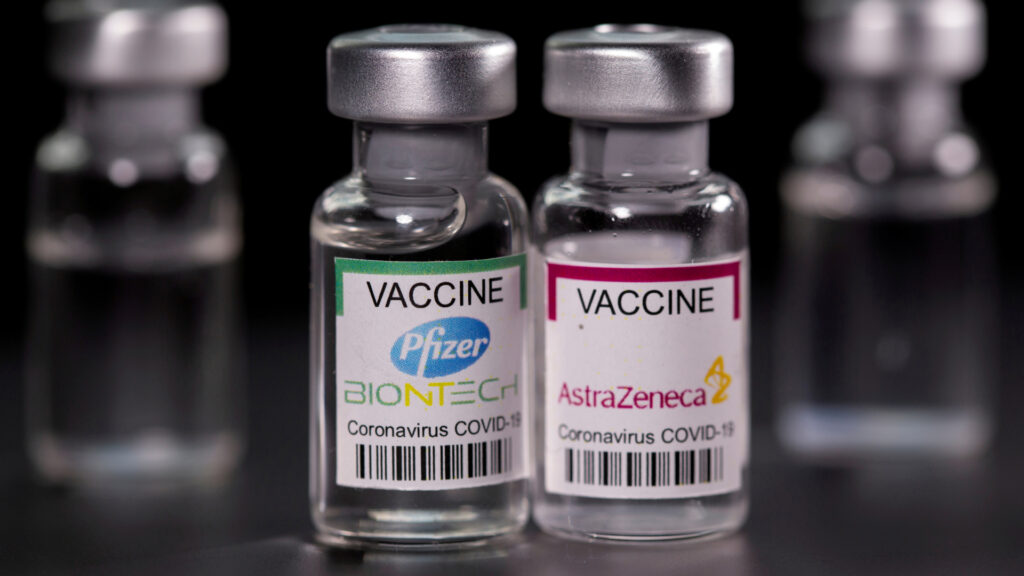
11. Pfizer or AstraZeneca
This is an example of industrial design rights for innovative medicine bottles in the healthcare industry.
Patented Design: Ergonomic injection bottles with tamper-proof caps for drug safety.
How It’s Protected: The bottle shape and visual safety systems are registered as innovative design elements under Industrial Design Rights.
Benefits for the Product:
- Prevents counterfeiting in the pharmaceutical industry.
- Boosts consumer trust in branded medications.
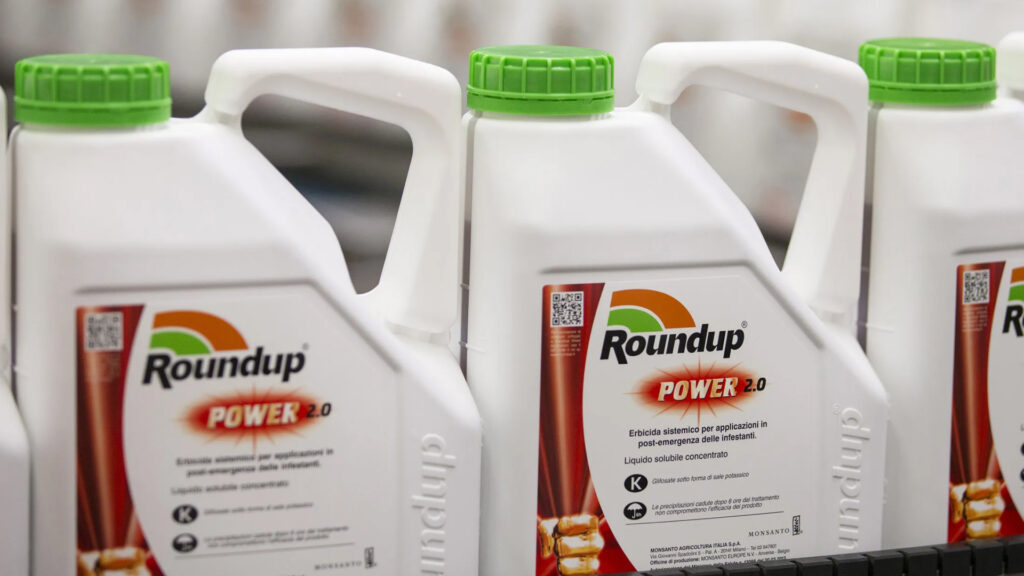
12. Bayer CropScience
This is an example of industrial design rights for chemical or pesticide bottles.
Patented Design: Ergonomic bottles with slanted necks for precise pouring of chemicals.
How It’s Protected: Bayer safeguards the design through Industrial Design Rights, focusing on both functional and visual advantages.
Benefits for the Product:
- Increases safety during the use of chemical products.
- Enhances user-friendliness and recognition in the agricultural market.
The Benefits of Having an Industrial Design Certificate for Companies
The examples above highlight the critical role Industrial Design Rights play in maintaining exclusivity and competitiveness in the market. Here are 10 key benefits companies can gain from registering Industrial Design Rights:
- Protection Against Imitation and Counterfeiting
- Competitive Advantage in the Market
- Enhanced Product and Brand Value
- Opportunities for Monetization via Licensing
- Strong Legal Protection
- Encouragement for Creativity and Innovation
- Attraction for Investors and Consumers
- Global Market Protection
- Optimized Branding and Product Identity
- Recognition of Business Innovation
Conclusion
By looking at the examples of Industrial Design Rights across various sectors, it’s clear how essential Industrial Design Rights are in protecting the aesthetic elements of a product. Companies that secure their industrial designs not only safeguard brand exclusivity but also build trust and loyalty with their customers over the long term.
If you want to safeguard your product designs, the first step is understanding the registration rules for Industrial Design Rights in your region. Don’t let your innovative designs fall victim to imitation!
FAQs: Industrial Design Rights
What are Industrial Design Rights?
Legal protections for the aesthetic aspects of a product, such as its shape, color, pattern, or visual features.
How long is the protection valid?
In Indonesia, Industrial Design Rights are valid for 10 years from the date of registration.
How do I register an industrial design?
Designs can be registered with the Directorate General of Intellectual Property (DJKI). This involves submitting design documents, completing registration forms, and paying administrative fees. It is recommended to use IP Law firm service like Widjojo to streamline the process
Are all design elements eligible for protection?
No, only elements that are unique and fulfill an aesthetic function are eligible.
Do Industrial Design Rights apply internationally?
Not directly. Registration must occur in individual countries or through international mechanisms, such as the Hague Agreement or the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).